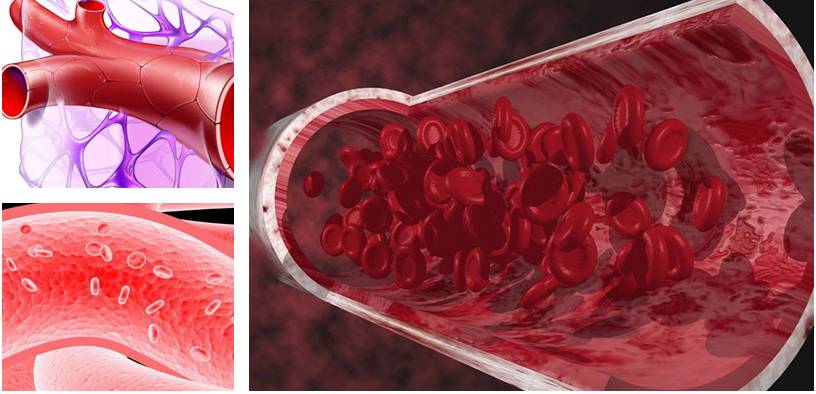
Blood vessels are conduits through which blood flows and are found all over the body. These network of pipes deliver life-giving nutrients to tissue and remove harmful metabolic wastes. Blood vessels are classified into three main types: arteries, veins, and capillaries. Arteries carry blood away from the heart while veins deliver blood to the heart. Between the arteries and veins are the capillaries, which represent a large surface area through which gases and nutrients are exchanged. Organisms differ in their vascular pattern. For example, open circulation creatures, like insects, have only arteries. Blood flows directly to body tissue and is retrieved by a hole in the heart. On the other hand, closed circulation creatures—such as mammals, birds, reptiles, and fish—rely on a network of arteries, veins, and capillaries to transport blood to and from the heart.